
A Guide to Air Compressor Pressure Regulation
Understanding how to effectively regulate the pressure of air compressors not only ensures operational efficiency but also extends the life of the equipment and enhances safety. Let’s delve into the essentials of air compressor pressure regulation, particularly for industrial-grade units.
Understanding Air Compressor Pressure
To effectively manage an air compressor system, understanding air compression is essential. This pressure, typically measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), is the force exerted by the compressed air.
Industrial air compressors are designed to operate at higher pressures than personal units, often exceeding 100 PSI, to meet the demands of industrial applications. The key is to maintain optimal pressure, as both under and over-pressurization can lead to inefficiencies and potential hazards.
Importance of Pressure Regulation
Pressure regulation in air compressors is critical for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures that the air delivered is at a consistent and appropriate pressure for specific tools and processes. Secondly, it contributes to energy efficiency.
Compressors consume a significant amount of energy, and improper pressure regulation can lead to wastage. Also, consistent pressure regulation prolongs the lifespan of the compressor and the tools it powers and minimizes the risk of safety hazards associated with over-pressurization.
Types of Pressure Regulation Systems for Industrial Air Compressors
Each pressure regulation system has its own advantages and is suited for different industrial applications. The choice of a pressure regulation component depends on factors like the size of the compressor, the nature of the application, energy efficiency requirements, and the desired level of precision in pressure control.
Below are some of the most common components:
Variable Speed Drive (VSD) Systems
Variable Speed Drive (VSD) systems adjust the motor speed in response to the demand for air. This method is highly efficient, as it reduces energy consumption by providing only the necessary amount of compressed air. VSD systems are known for their ability to maintain a stable pressure band, making them ideal for applications with varying air demands.
Load/Unload Control Systems
Load/Unload control systems are common in industrial settings. These systems allow the compressor to run continuously while modulating its capacity to produce air. When demand is low, the compressor unloads, reducing its capacity and saving energy. This type of system is suitable for applications with fluctuating air demand.
Modulation Control Systems
Modulation control systems offer another method of pressure regulation. These systems adjust the compressor’s inlet valve to control the amount of air being compressed, effectively modulating the compressor’s output. While not as energy-efficient as VSD systems, modulation control is beneficial for applications with steady demand.
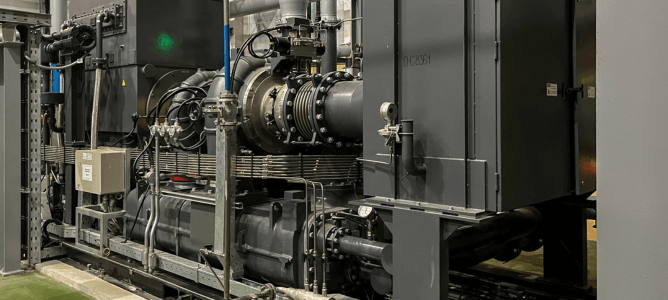
Understanding Air Compressor Components
Each component plays a specific and vital role in the operation of an air compressor. Proper air compressor maintenance of these components ensures efficient, safe, and long-lasting compressor performance.
Compressor Pump: The heart of an air compressor, the pump is responsible for compressing air. It draws in atmospheric air, and by decreasing its volume, the pump increases the pressure of the air. Compressor pumps can be of various types like piston-type, rotary screw, or centrifugal, and the choice depends on the required pressure and flow rate.
Pressure Gauges: These are critical for monitoring the air compressor’s performance. One gauge usually measures the tank pressure (showing how much air is currently stored), while another measures the outlet pressure (the pressure at which air is being supplied to the tools or systems).
Pressure Switch: This component turns the motor on and off based on the air pressure in the tank. When the pressure drops below a preset level, the switch activates the motor to refill the tank. When the desired pressure is reached, it turns the motor off.
Regulators: These are used to control the air pressure coming out of the tank to the air tool or application. Regulators allow the user to set the desired output pressure, which can be lower than the tank pressure.
Safety Valve: An essential safety component, the safety valve is designed to open if the tank pressure exceeds safe limits. This prevents accidents due to over-pressurization.
Air Filter: Air drawn into the compressor is filtered to remove impurities, dust, and moisture. This ensures that the air delivered is clean and prevents damage to the tools and equipment using the compressed air.

Steps to Regulate Pressure
The following are some key steps for pressure regulation in industrial air compressors:
- Understand the Pressure Requirements of Tools. Before adjusting the compressor, know the pressure requirements of the tools you’ll be using. Most tools have their optimal operating pressure specified by the manufacturer.
- Locate the Pressure Regulator Knob. The pressure regulator on an air compressor is typically a knob located on the control panel of the compressor. This knob controls the amount of pressure that is allowed to flow from the compressor into the air hose and tools.
- Check the Current Pressure Level. Before making adjustments, check the current pressure level displayed on the compressor’s gauge. This gauge indicates the pressure of the air currently being output from the compressor.
- Adjust the Regulator. To adjust the pressure, turn the regulator knob. Turning it clockwise typically increases the pressure, while turning it counterclockwise decreases it. Make these adjustments slowly and in small increments, especially when increasing pressure.
- Test Tool Performance. Once you’ve set the desired pressure, test your tool. Connect the tool to the compressor via the air hose, and ensure it operates effectively at the adjusted pressure. If the performance is not optimal, you may need to readjust the pressure slightly.
- Use Safety Precautions. Never exceed the maximum pressure rating of the air compressor, the air hose, or the pneumatic tool. Exceeding these limits can be dangerous and may lead to equipment failure or personal injury.
- Perform Regular Checks and Maintenance. Regularly check the compressor’s settings before each use. Over time, vibrations can cause the regulator knob to shift, altering the pressure settings. Additionally, air compressor audits, including checking for leaks and ensuring proper lubrication, will help maintain consistent pressure regulation.
Explore NiGen’s Range of Industrial Air Compressor Solutions
NiGen offers a wide array of industrial air compressor solutions catering to diverse industrial needs. NiGen’s products are designed with advanced pressure regulation technologies, ensuring efficient and safe operation. Ready to get started?
